Ventilation Therapy
Ventilation therapy is a medical treatment that utilizes a ventilator to aid or substitute spontaneous breathing in individuals who cannot breathe sufficiently on their own. This therapy plays a vital role in delivering oxygen to the lungs and eliminating carbon dioxide from the body, offering essential respiratory support for patients facing respiratory challenges. Breathing involves two key components: ventilation and respiration. A ventilator device can assist in enhancing the effectiveness of both processes.
- Ventilation: the movement of air in and out of your lungs.
- Respiration: the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
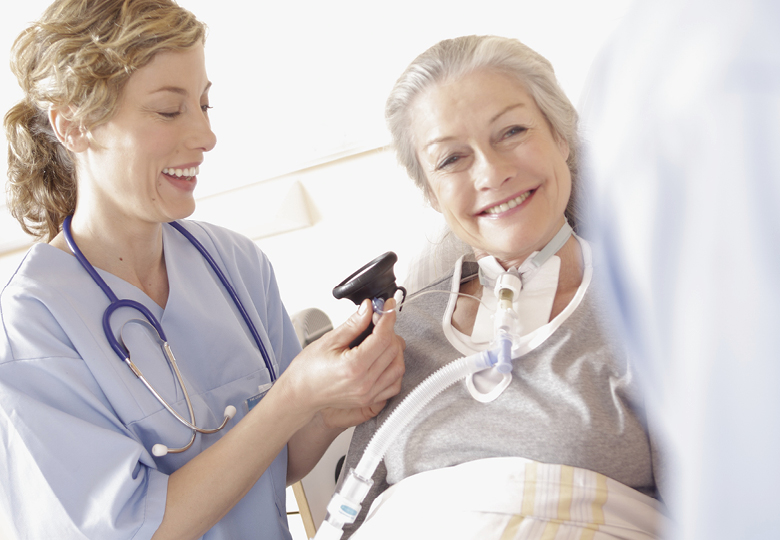

Types of Mechanical Ventilation
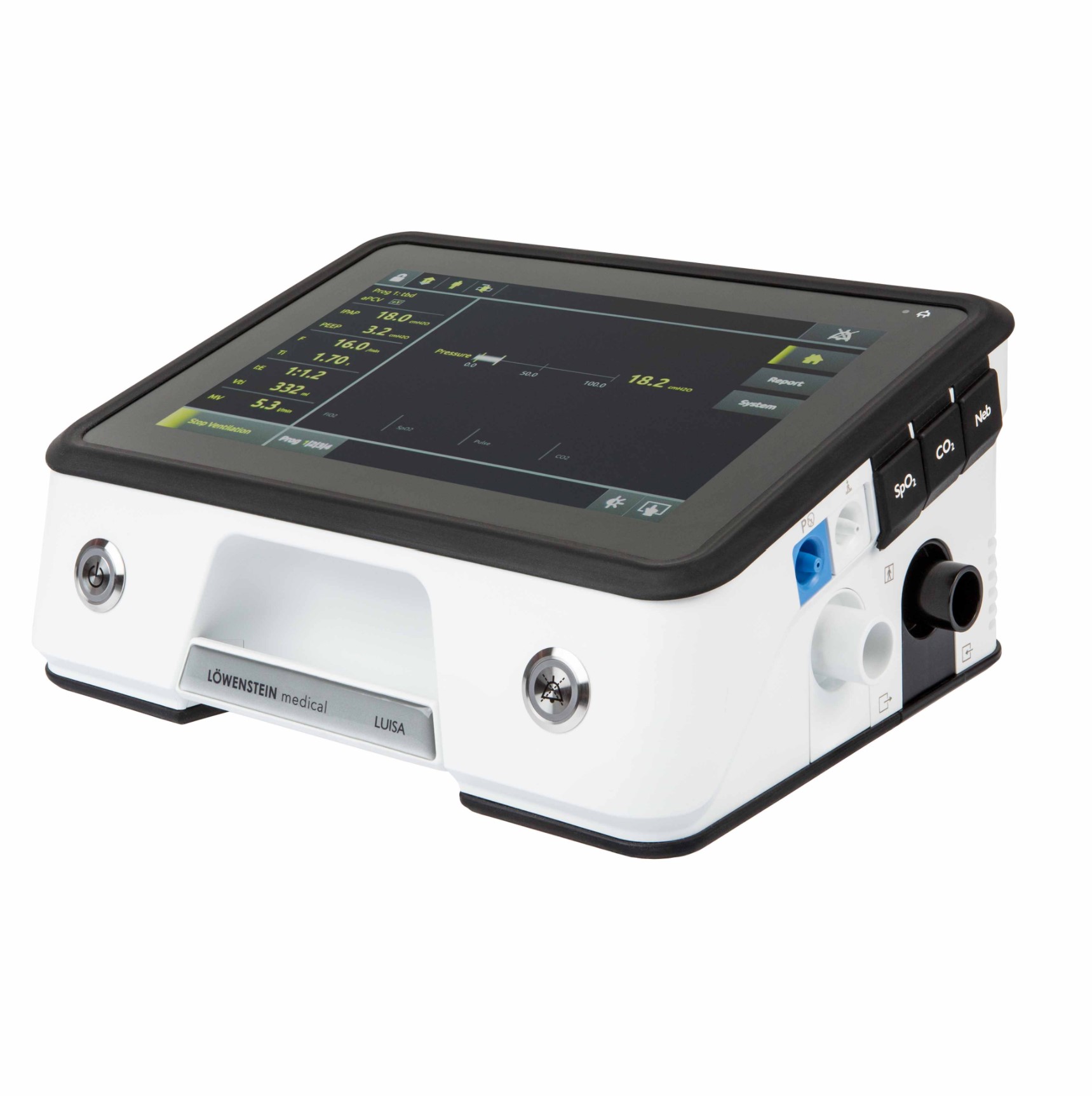
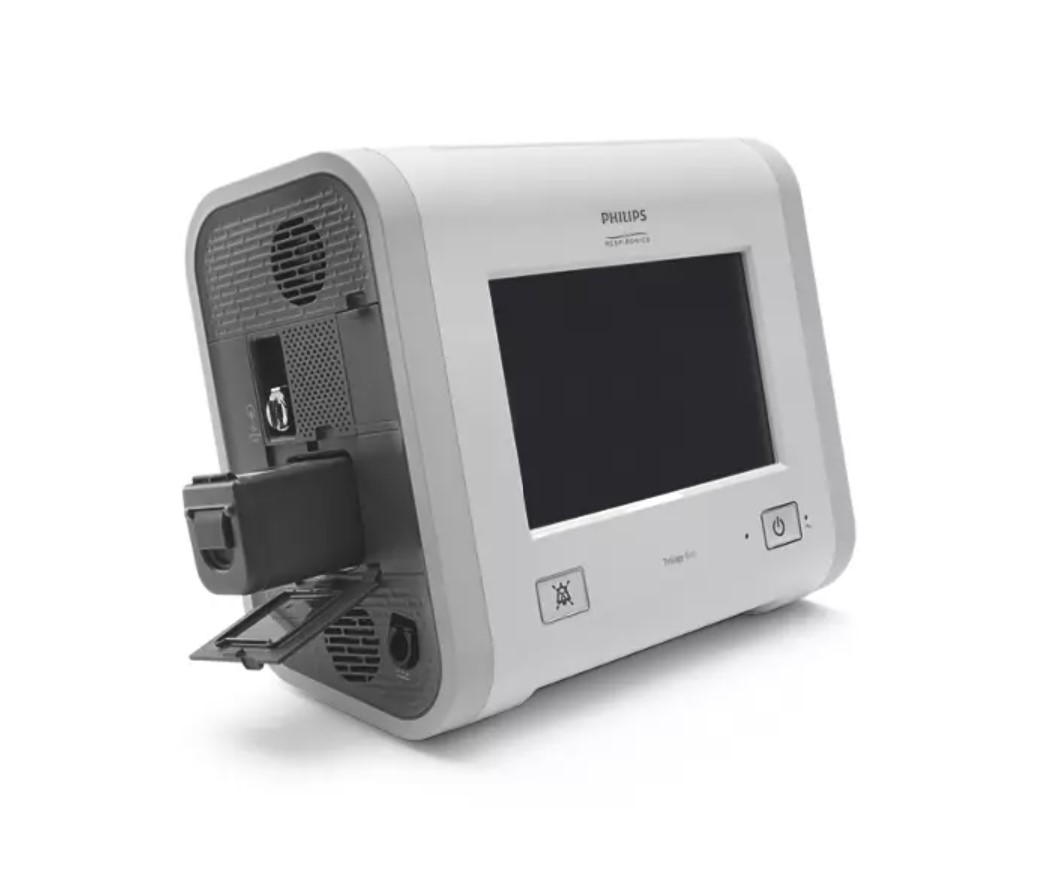
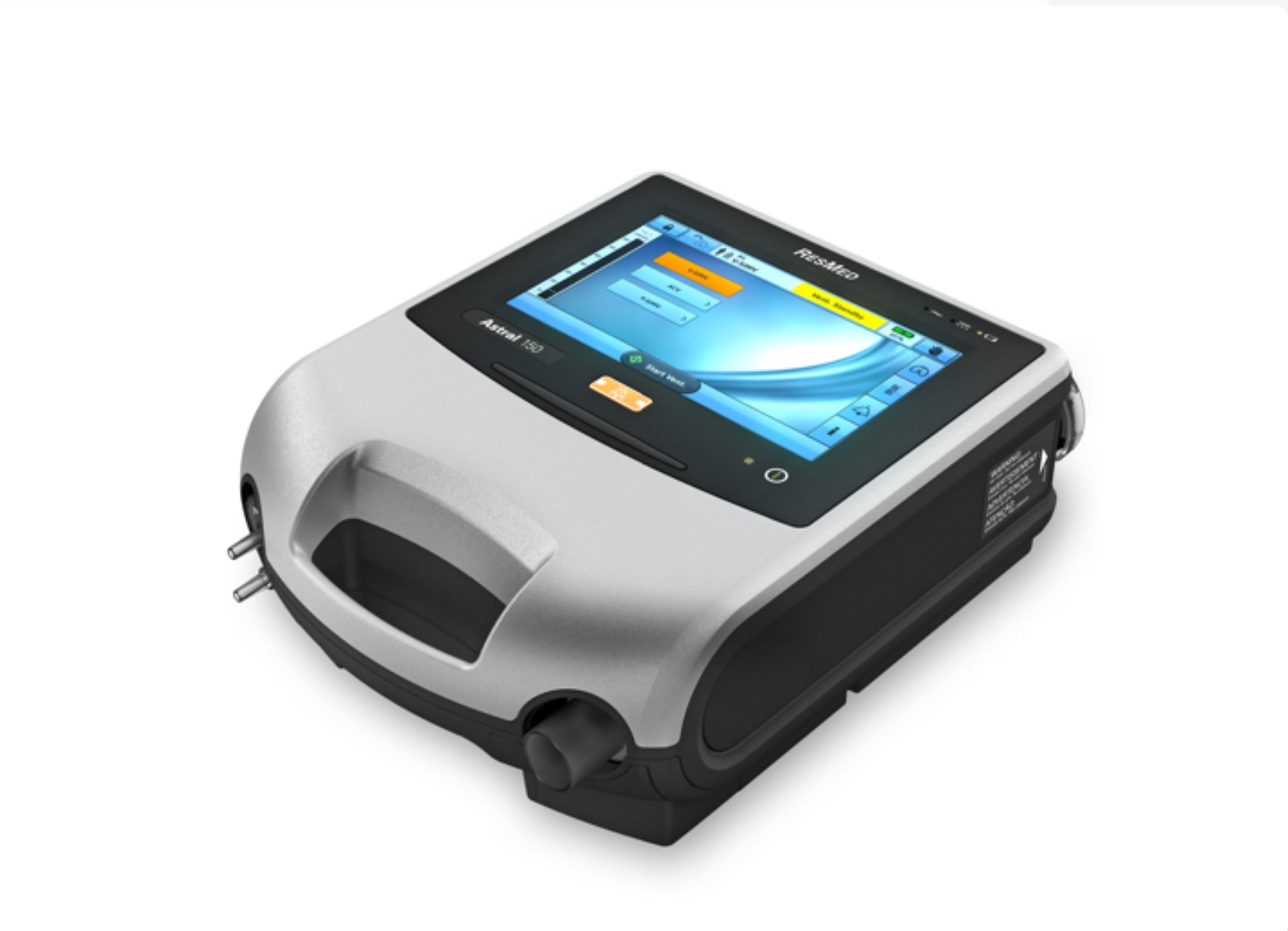
Invasive Ventilation: is a treatment method that involves delivering positive pressure to the lungs through an endotracheal or tracheostomy tube attached to a ventilator. This method regulates the patient's breathing by providing a specific air mixture to the lungs, thereby enabling or supporting lung function and facilitating gas exchange.
Noninvasive Ventilation (NHV): is a treatment method that provides positive pressure airflow to the lungs via a mask or mouthpiece linked to a ventilator. This technique aids the patient's breathing by delivering a prescribed mixture of air into the lungs, thereby enhancing lung function and facilitating gas exchange.
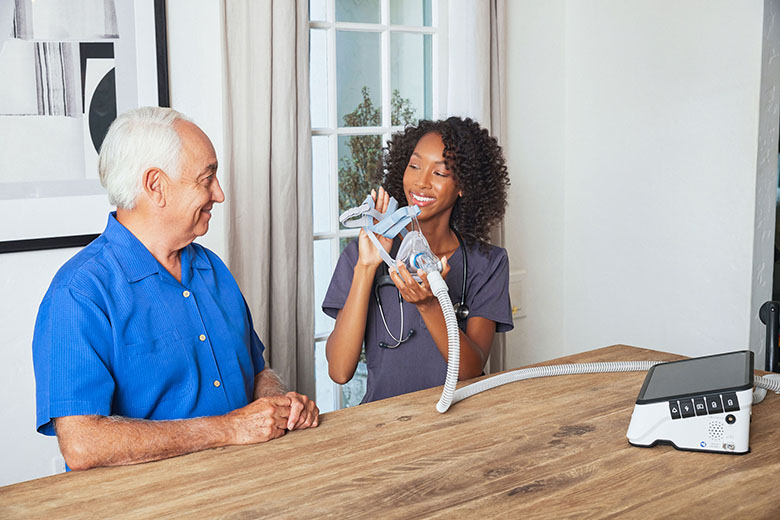

Benefits of Home Ventilation Therapy
Ventilation therapy may provide several benefits, including:
- Better Breathing: Home ventilation helps with delivering oxygen to the lungs and removing carbon dioxide from the body and helps keep airways open.
- Increase Activity: Home ventilation devices are portable and can help patients become more active during the day.
- Reduce Hospital Stays: Ventilation therapy can help stabilize a patient’s condition allowing for earlier intervention and faster recovery leading to shorter hospital stays.
- Reduce Hospital Re-Admission: Patients might transition to using a ventilator at home, enabling them to manage their breathing in a familiar environment. This approach provides essential support and has the potential to decrease the likelihood of being readmitted to the hospital.